Eu closer to blockbuster investment domestic semiconductor chip production – EU Closer to Blockbuster Investment in Domestic Semiconductor Chip Production sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The European Union is on the verge of making a monumental investment in its domestic semiconductor chip production, a move that could reshape the global technology landscape.
This ambitious plan aims to bolster the EU’s technological independence, strengthen its economic competitiveness, and address critical supply chain vulnerabilities.
This investment is driven by a number of factors, including the growing demand for semiconductors, the increasing geopolitical tensions surrounding chip production, and the EU’s desire to become a global leader in advanced technologies. The scale of the investment is unprecedented, with billions of euros being allocated to support the construction of new chip fabrication facilities, research and development, and talent development programs.
This ambitious undertaking will have far-reaching consequences for the EU’s semiconductor industry, its economy, and its geopolitical standing.
EU’s Semiconductor Ambitions: Eu Closer To Blockbuster Investment Domestic Semiconductor Chip Production
The European Union (EU) is actively pursuing a strategy to bolster its domestic semiconductor production capabilities. This ambitious initiative aims to strengthen Europe’s technological sovereignty and reduce its reliance on external suppliers. The EU’s focus on chip manufacturing is driven by a combination of strategic, economic, and geopolitical considerations.
Rationale for EU’s Focus on Chip Manufacturing
The EU’s decision to prioritize semiconductor production stems from its recognition of the critical role chips play in modern economies and societies. Semiconductors are the building blocks of virtually all electronic devices, from smartphones and computers to cars and industrial equipment.
The EU’s reliance on external suppliers, primarily in Asia, has exposed its vulnerabilities to supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions.
Key Drivers of the EU’s Investment Push
The EU’s investment push in semiconductor production is driven by several key factors:
- Strategic Importance:Semiconductors are considered a strategic asset, essential for technological innovation, economic growth, and national security. The EU aims to secure its access to these critical components and reduce its dependence on other regions.
- Economic Growth:Semiconductor production is a high-value industry that generates significant economic activity, creating jobs and driving innovation. The EU aims to attract investment and foster the growth of a vibrant domestic semiconductor ecosystem.
- Geopolitical Considerations:The global semiconductor landscape is increasingly influenced by geopolitical factors. The EU seeks to reduce its reliance on external suppliers and ensure its access to critical technologies in a volatile world.
- Technological Sovereignty:The EU’s ambition to regain technological sovereignty is a driving force behind its semiconductor strategy. The EU aims to become a global leader in semiconductor research, development, and manufacturing, fostering innovation and competitiveness.
The ‘Blockbuster’ Investment
The EU’s ambition to become a global leader in semiconductor production is not just a declaration but a commitment backed by a significant financial investment. This “blockbuster” investment, as it’s being called, is intended to bridge the gap between the EU’s current semiconductor capabilities and its aspirations.
Scale and Scope of the Investment
The EU’s investment plan is designed to be a multi-pronged approach, addressing both the short-term need for chip supply and the long-term goal of building a resilient and competitive semiconductor ecosystem. The plan includes:* €43 billion investment:This funding will be allocated to various initiatives, including research and development, manufacturing infrastructure, and talent development.
Public-private partnerships
The EU is encouraging collaboration between governments, research institutions, and private companies to accelerate innovation and technology transfer.
Attracting foreign investment
The EU is actively seeking to attract foreign investment in semiconductor production facilities within its borders.
Impact on the EU Semiconductor Industry
This significant investment is expected to have a profound impact on the EU’s semiconductor industry, creating a ripple effect across the entire value chain. Some key impacts include:* Boosting domestic production:The investment is expected to increase the EU’s share of global semiconductor production, reducing its reliance on external suppliers.
Creating new jobs
The semiconductor industry is a major job creator, and the EU’s investment is expected to generate thousands of new jobs in research, manufacturing, and supporting services.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about 5 top tips to land your dream tech job in .
Driving innovation
The investment will foster research and development in cutting-edge semiconductor technologies, putting the EU at the forefront of innovation.
Comparison with Other Regions
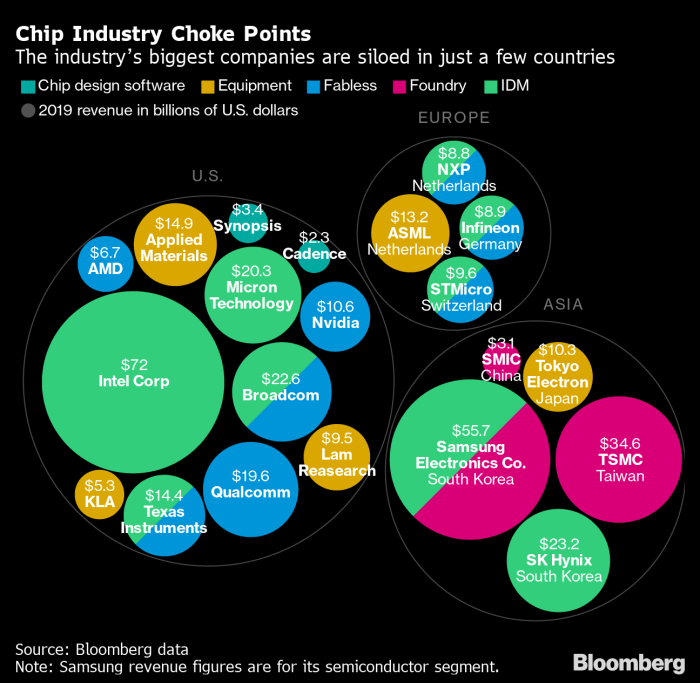
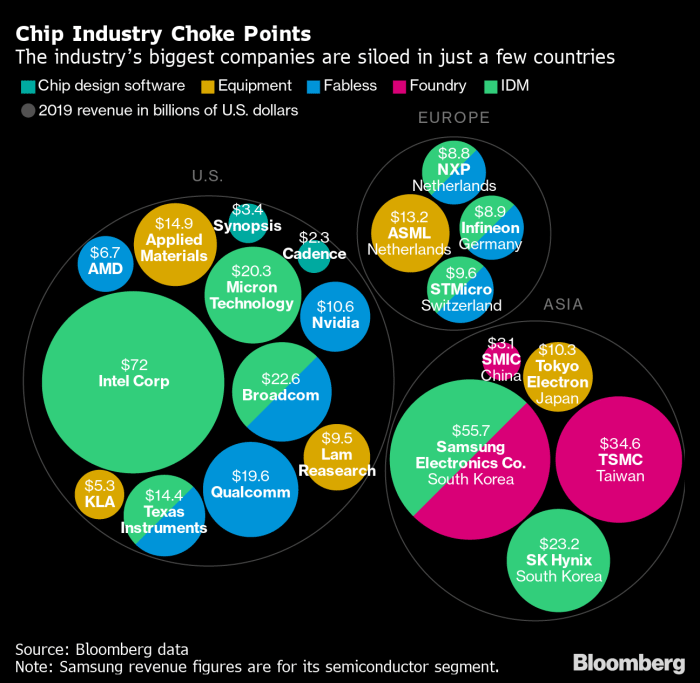
The EU’s investment plan is comparable to similar initiatives in other regions, such as the US’s CHIPS Act and China’s National Integrated Circuit Industry Development Fund. These initiatives reflect the global recognition of the strategic importance of semiconductors and the need to secure domestic production.* US CHIPS Act:This $52 billion act aims to boost domestic semiconductor production and research, with a focus on attracting foreign investment.
China’s National Integrated Circuit Industry Development Fund
This fund provides financial support to Chinese companies involved in semiconductor design, manufacturing, and equipment.The EU’s investment plan is a bold step towards securing its semiconductor future. By creating a robust domestic ecosystem, the EU aims to become a major player in the global semiconductor industry, contributing to its own economic growth and technological leadership.
Key Players and Partnerships
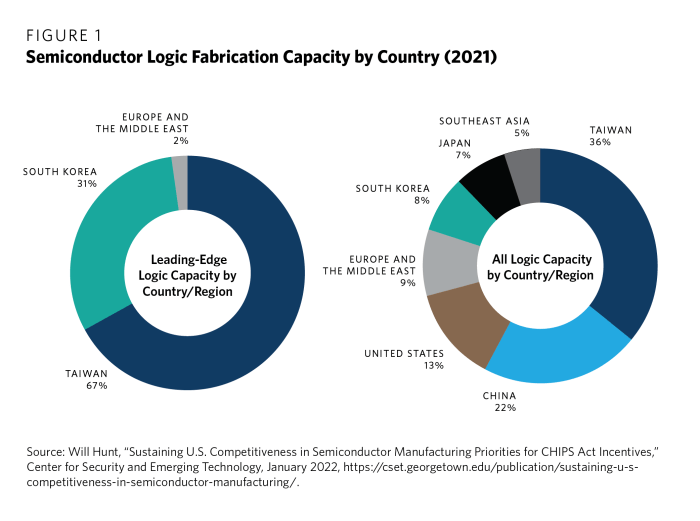
The EU’s semiconductor ambitions are not a solo effort; they are driven by a network of key players and partnerships, both within the EU and beyond. This collaborative approach is crucial to securing the necessary resources, expertise, and market access to achieve the ambitious goals Artikeld in the European Chips Act.
Public-Private Partnerships, Eu closer to blockbuster investment domestic semiconductor chip production
Public-private partnerships are a cornerstone of the EU’s semiconductor strategy. These partnerships bring together the financial resources of the public sector with the technological expertise and market reach of private companies.
- The European Chips Act itself allocates €43 billion in public funding for semiconductor research, development, and production. This funding is expected to leverage significant private investment, creating a powerful multiplier effect.
- The European Investment Bank (EIB) is a key player in financing semiconductor projects, providing loans and guarantees to support both large-scale manufacturing facilities and smaller, more specialized companies.
- The European Innovation Council (EIC) provides funding for innovative semiconductor technologies through its grant schemes and accelerator programs. These programs aim to support the development of next-generation chips and technologies that will be crucial for future competitiveness.
Collaboration Between EU Member States
The EU’s semiconductor ambitions are also being driven by collaboration between member states.
- The “European Chips Alliance” is a platform for collaboration between member states, research institutions, and industry players. This alliance facilitates knowledge sharing, joint research projects, and the development of common strategies to strengthen the EU’s semiconductor ecosystem.
- Several member states have established national semiconductor strategies, which complement the EU-wide approach and provide tailored support for local industry and research activities. These national strategies often focus on specific areas of expertise or production capabilities, creating a diverse and interconnected semiconductor ecosystem within the EU.
Technological Focus and Innovation
The EU’s semiconductor investment aims to foster a robust and competitive domestic chip industry, focusing on key technologies and applications with significant economic and strategic value. The initiative encompasses a broad range of technologies, from advanced manufacturing and automation to cutting-edge research and development, with a strong emphasis on innovation and collaboration.
Advanced Node Technologies
The investment prioritizes the development and production of advanced node technologies, which are crucial for powering high-performance computing, artificial intelligence, and other demanding applications. These technologies involve shrinking the size of transistors on chips, leading to increased performance, energy efficiency, and processing power.
- EUV Lithography:The investment supports the development and deployment of extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography, a critical technology for producing chips with features smaller than 10 nanometers. This technology is essential for achieving the performance and efficiency gains required for next-generation computing and data processing.
- FinFET and GAAFET Transistors:The initiative also focuses on the development and production of advanced transistor designs, such as FinFET and GAAFET, which offer improved performance and power efficiency compared to traditional planar transistors. These technologies are essential for pushing the boundaries of chip performance and enabling the development of next-generation computing systems.
Emerging Technologies
The EU’s semiconductor strategy recognizes the importance of emerging technologies, such as quantum computing, neuromorphic computing, and photonics, which have the potential to revolutionize computing and data processing.
- Quantum Computing:The investment supports the development of quantum computing technologies, which leverage quantum phenomena to perform calculations that are impossible for classical computers. Quantum computers have the potential to solve complex problems in fields such as drug discovery, materials science, and cryptography.
- Neuromorphic Computing:The initiative also focuses on neuromorphic computing, which mimics the structure and function of the human brain to develop more efficient and powerful computing systems. Neuromorphic chips are designed to handle complex tasks, such as image recognition, natural language processing, and real-time decision-making.
- Photonics:The investment supports the development and production of photonic chips, which use light instead of electrons to transmit and process information. Photonic chips offer faster speeds, lower power consumption, and greater bandwidth compared to traditional electronic chips.
Research and Development
The EU’s semiconductor strategy recognizes the crucial role of research and development in driving innovation and competitiveness. The investment supports a wide range of research initiatives, including:
- Fundamental Research:The investment funds fundamental research in areas such as materials science, device physics, and computational design, laying the foundation for future technological advancements.
- Applied Research:The initiative also supports applied research in areas such as chip design, manufacturing processes, and packaging technologies, accelerating the development of new and improved semiconductor products.
Advanced Manufacturing and Automation
The EU’s semiconductor investment emphasizes the importance of advanced manufacturing and automation in achieving cost-efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness. The initiative supports the development and deployment of cutting-edge manufacturing technologies, including:
- High-Volume Manufacturing:The investment supports the development of high-volume manufacturing processes, ensuring that the EU can meet the growing demand for semiconductors. This involves investing in state-of-the-art equipment, facilities, and skilled personnel.
- Automation and Robotics:The initiative also supports the adoption of automation and robotics in semiconductor manufacturing, reducing labor costs, improving productivity, and enhancing product quality. This includes investing in advanced robotics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence systems.
Economic and Geopolitical Implications
The EU’s ambitious semiconductor investment plan holds the potential to reshape the global tech landscape, bringing about significant economic and geopolitical implications. This strategy aims to boost domestic chip production, reduce reliance on external suppliers, and strengthen Europe’s position in the technological race.
Economic Benefits of Increased Semiconductor Production
The increased semiconductor production in the EU promises a wide range of economic benefits.
- Job creation:The semiconductor industry is a major job creator, with a complex supply chain involving design, manufacturing, and packaging. Increased production would lead to the creation of new jobs across various sectors, contributing to economic growth and prosperity.
- Technological innovation:Domestic chip production fosters a thriving ecosystem of innovation. It encourages research and development, leading to the creation of new technologies and products that can drive economic competitiveness and create new markets.
- Increased competitiveness:By reducing reliance on foreign suppliers and boosting domestic production, the EU aims to become more competitive in the global tech market. This could lead to increased exports, attracting foreign investment, and strengthening the EU’s overall economic standing.
- Reduced reliance on foreign suppliers:The EU’s strategy aims to mitigate the risks associated with supply chain disruptions, particularly in times of geopolitical instability. By increasing domestic production, the EU can reduce its reliance on foreign suppliers and ensure a more stable and resilient supply of essential components.
Geopolitical Significance of the EU’s Chip Strategy
The EU’s semiconductor strategy is not merely an economic initiative but also a geopolitical move aimed at strengthening Europe’s position in the global tech landscape.
- Strategic autonomy:The EU aims to achieve greater strategic autonomy in the tech sector, reducing its dependence on other countries, particularly the United States and China, for critical technologies. This is crucial for maintaining national security and economic independence.
- Strengthened partnerships:The EU’s chip strategy encourages collaboration with other countries and regions, fostering partnerships that promote shared technological advancements and reduce reliance on individual players. This can lead to a more balanced and interconnected global tech ecosystem.
- Global leadership:By investing in semiconductor production and research, the EU aims to regain its position as a global leader in the tech sector. This can influence global standards, promote innovation, and attract talent and investment from around the world.
Implications for Global Supply Chains and Trade
The EU’s semiconductor strategy has significant implications for global supply chains and trade.
- Reshaping global supply chains:The EU’s efforts to boost domestic production could lead to a more diversified and resilient global semiconductor supply chain. This would reduce reliance on single production hubs and create new opportunities for manufacturers and suppliers around the world.
- Increased competition:The EU’s strategy could lead to increased competition in the global semiconductor market, potentially driving down prices and benefiting consumers. However, it could also lead to trade tensions and disputes, particularly if the EU adopts protectionist measures to protect its domestic industry.
- New trade agreements:The EU’s semiconductor strategy may lead to new trade agreements and partnerships with countries that share similar goals of promoting domestic chip production and strengthening their tech sectors. This could create new opportunities for collaboration and economic growth.
Challenges and Opportunities
The EU’s ambitious semiconductor investment, while promising, faces several challenges that require careful consideration and strategic planning. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial for the success of this initiative, which holds the potential to reshape the EU’s economic and technological landscape.
Addressing the Challenges
The EU’s semiconductor ambitions are not without their challenges. These hurdles need to be addressed strategically to ensure the success of this initiative.
- Talent Acquisition and Development:The semiconductor industry requires a highly skilled workforce, which the EU may struggle to attract and retain, especially in competition with other regions like the US and Asia. This necessitates targeted training programs, educational initiatives, and incentives to develop a robust talent pool.
- Research and Development:Maintaining a leading edge in semiconductor technology requires continuous investment in research and development (R&D). The EU needs to foster collaboration between universities, research institutions, and industry to drive innovation and develop cutting-edge technologies.
- Supply Chain Resilience:The EU’s reliance on global supply chains for critical components and materials makes its semiconductor industry vulnerable to disruptions. Establishing a more resilient and diversified supply chain is essential to mitigate risks and ensure the long-term sustainability of the sector.
- Market Access and Competition:The EU’s semiconductor industry faces stiff competition from established players in Asia and the US. The EU needs to develop strategies to gain market share and ensure fair competition, leveraging its strengths in design and innovation.
- Funding and Investment:Securing sufficient funding for the ambitious investment plan is crucial. This requires attracting private investment, leveraging public funds, and creating an attractive environment for venture capital and other forms of financing.
Opportunities for Growth
Despite the challenges, the EU’s semiconductor investment presents significant opportunities for economic growth and technological advancement.
- Job Creation and Economic Growth:The investment is expected to create thousands of new jobs in the semiconductor sector and related industries, boosting economic growth and creating new opportunities for EU citizens.
- Technological Leadership:By focusing on advanced technologies like AI and quantum computing, the EU can establish itself as a global leader in these emerging fields, fostering innovation and attracting talent.
- Strategic Autonomy:This investment strengthens the EU’s technological independence and reduces its reliance on other regions for critical technologies, enhancing its strategic autonomy and resilience.
- Innovation Ecosystem:The investment will foster a vibrant ecosystem of innovation, attracting startups, research institutions, and industry players, creating a dynamic and competitive environment.
- Digital Transformation:The availability of advanced semiconductors will accelerate the EU’s digital transformation, driving innovation in areas like cloud computing, data analytics, and artificial intelligence.