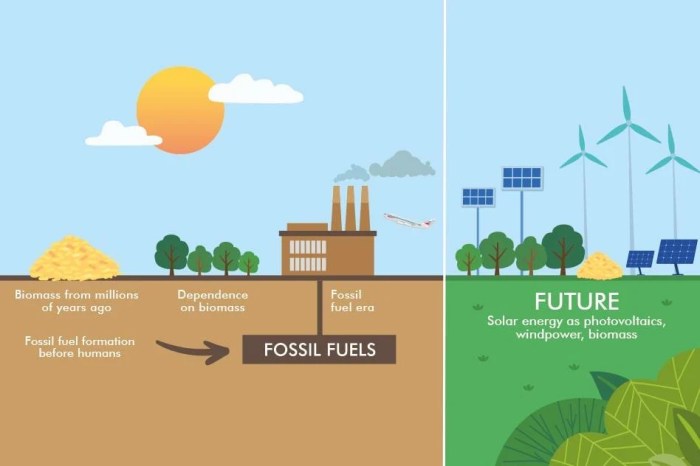
Energy more sustainable in * – Energy More Sustainable in Our Future is a journey into the heart of our global energy landscape, exploring the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead as we strive for a cleaner, more sustainable energy system. This journey delves into the fascinating world of renewable energy technologies, exploring their strengths, weaknesses, and the exciting potential they hold for the future.
From solar panels soaking up the sun’s rays to wind turbines harnessing the power of the wind, we’ll uncover the diverse array of technologies that are transforming the way we generate and consume energy. We’ll also delve into the critical role of energy efficiency and conservation, exploring practical strategies to reduce our energy footprint and create a more sustainable future.
The Global Energy Landscape

The global energy landscape is in a state of flux, driven by a confluence of factors including population growth, economic development, and the pressing need to address climate change. Understanding the current state of global energy production and consumption, as well as the challenges and opportunities associated with transitioning to a more sustainable energy system, is crucial for shaping a more secure and environmentally responsible future.
Current State of Global Energy Production and Consumption
The world’s energy demand is steadily increasing, primarily driven by economic growth and population expansion. Fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas, continue to dominate the global energy mix, accounting for around 80% of total energy production. This reliance on fossil fuels poses significant environmental challenges, including greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and climate change.
- Coalremains a significant source of energy, particularly in Asia, where it accounts for over 50% of electricity generation. However, coal is the most carbon-intensive fossil fuel, making it a major contributor to climate change.
- Oilis the dominant fuel for transportation, accounting for over 90% of global road transport energy. The world’s reliance on oil makes it vulnerable to price fluctuations and geopolitical instability.
- Natural gasis considered a cleaner alternative to coal and oil, emitting less carbon dioxide per unit of energy. However, natural gas extraction and transportation can have environmental impacts, including methane leaks.
Challenges and Opportunities for Transitioning to a More Sustainable Energy System
The transition to a more sustainable energy system presents both challenges and opportunities. Key challenges include:
- Infrastructure Investment:Shifting to renewable energy sources requires substantial investment in new infrastructure, such as solar and wind farms, energy storage systems, and smart grids.
- Intermittency of Renewable Energy Sources:Solar and wind energy are intermittent sources, meaning their availability depends on weather conditions. This requires developing reliable energy storage solutions to ensure a consistent supply of electricity.
- Technological Advancements:Continued innovation in energy technologies, such as battery storage and carbon capture and storage, is essential to enhance the efficiency and affordability of renewable energy.
- Policy and Regulatory Frameworks:Governments need to establish clear policies and regulatory frameworks that incentivize renewable energy development and promote energy efficiency.
Despite these challenges, the transition to a sustainable energy system offers significant opportunities:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions:Replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy sources can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating climate change.
- Enhanced Energy Security:Diversifying energy sources reduces dependence on fossil fuels and volatile global markets, enhancing energy security.
- Economic Growth:The renewable energy sector is a rapidly growing industry, creating new jobs and economic opportunities.
- Improved Air Quality:Reducing reliance on fossil fuels can improve air quality, reducing respiratory illnesses and improving public health.
The Role of Renewable Energy Sources in Addressing Energy Security and Climate Change Concerns
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass, play a critical role in addressing energy security and climate change concerns.
- Solar Energy:Solar energy is a clean and abundant source of energy that can be harnessed through photovoltaic panels and concentrated solar power plants. It is becoming increasingly cost-effective and is rapidly expanding globally.
- Wind Energy:Wind energy is another clean and renewable source of energy that is becoming increasingly cost-competitive with fossil fuels. Wind turbines are deployed on land and offshore, harnessing the power of wind to generate electricity.
- Hydropower:Hydropower is a mature renewable energy source that relies on the flow of water to generate electricity. However, hydropower projects can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat loss and changes in water flow.
- Geothermal Energy:Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from the Earth’s interior to generate electricity. It is a reliable and sustainable source of energy, but it is geographically limited to areas with geothermal resources.
- Biomass Energy:Biomass energy is derived from organic matter, such as wood, crops, and waste. It can be used for heating, electricity generation, and biofuels. However, biomass energy can have environmental impacts, including deforestation and greenhouse gas emissions.
Sustainable Energy Technologies

The transition to a sustainable energy future hinges on the development and deployment of various renewable energy technologies. These technologies harness natural resources like sunlight, wind, water, and geothermal heat to generate clean and sustainable energy. This section will delve into the different types of renewable energy technologies, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages, and exploring emerging technologies that are shaping the future of sustainable energy.
Solar Energy
Solar energy is a versatile and abundant renewable energy source that converts sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells or solar thermal systems.
Explore the different advantages of uk researchers used ai uncover a whopping 11456 social innovation projects online that can change the way you view this issue.
- Photovoltaic (PV) Cells:PV cells are semiconductor devices that directly convert sunlight into electricity through the photoelectric effect. These cells are typically arranged in panels and used for residential, commercial, and utility-scale power generation.
- Solar Thermal Systems:Solar thermal systems use sunlight to heat water or air for various applications, including residential water heating, space heating, and industrial processes. They work by using mirrors or collectors to concentrate sunlight and heat a fluid, which then transfers heat to a storage system or directly to the desired application.
Advantages of Solar Energy:
- Abundant and Free:Sunlight is a readily available and free resource, making solar energy a sustainable and cost-effective option.
- Clean and Environmentally Friendly:Solar energy does not produce greenhouse gases or air pollutants, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Low Maintenance:Solar panels typically require minimal maintenance, reducing operational costs.
- Versatile Applications:Solar energy can be used for a wide range of applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial power generation, water heating, and space heating.
Disadvantages of Solar Energy:
- Intermittency:Solar energy generation is dependent on sunlight, which is intermittent and varies with weather conditions.
- Land Requirements:Large-scale solar farms require significant land areas, which can raise concerns about land use and habitat fragmentation.
- Initial Cost:The initial investment for solar panels can be high, although government incentives and falling prices are making it more affordable.
- Weather Dependence:Solar energy generation is affected by cloud cover, rain, and snow, reducing efficiency during adverse weather conditions.
Wind Energy
Wind energy harnesses the kinetic energy of wind to generate electricity using wind turbines. Wind turbines consist of blades that rotate when exposed to wind, driving a generator that produces electricity. Wind energy is a rapidly growing renewable energy source, with significant potential for large-scale power generation.
Advantages of Wind Energy:
- Abundant and Renewable:Wind is a readily available and renewable resource, making wind energy a sustainable and reliable source of power.
- Clean and Environmentally Friendly:Wind energy does not produce greenhouse gases or air pollutants, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Cost-Effective:The cost of wind energy has significantly decreased in recent years, making it a competitive alternative to fossil fuels.
- Job Creation:The wind energy industry creates numerous jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
Disadvantages of Wind Energy:
- Intermittency:Wind energy generation is dependent on wind speed, which can vary significantly, leading to intermittency in power supply.
- Visual Impact:Wind turbines can have a visual impact on the landscape, raising aesthetic concerns in some areas.
- Noise Pollution:Wind turbines can produce noise, which can be a concern for nearby residents.
- Bird and Bat Mortality:Wind turbines can pose a risk to birds and bats, although mitigation measures are being implemented to minimize impacts.
Hydropower
Hydropower is a mature renewable energy technology that uses the flow of water to generate electricity. Hydropower plants typically consist of a dam or reservoir that stores water, which is then released through turbines to generate electricity. Advantages of Hydropower:
- Reliable and Predictable:Hydropower is a reliable and predictable energy source, as water flow can be controlled and managed.
- Clean and Environmentally Friendly:Hydropower does not produce greenhouse gases or air pollutants, making it a clean and sustainable energy source.
- Multiple Benefits:Hydropower plants can provide multiple benefits, including flood control, irrigation, and recreation.
- Long Lifespan:Hydropower plants have a long lifespan, making them a long-term investment.
Disadvantages of Hydropower:
- Environmental Impacts:Dam construction can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat fragmentation, water flow disruption, and sedimentation.
- High Initial Cost:Hydropower plants require significant capital investment for construction and infrastructure.
- Limited Geographic Availability:Hydropower is only feasible in areas with sufficient water resources and suitable topography.
- Social and Economic Impacts:Dam construction can displace communities and impact local economies.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from the Earth’s interior to generate electricity or provide direct heating. Geothermal power plants use steam or hot water from underground reservoirs to drive turbines and generate electricity. Geothermal heat pumps use the Earth’s constant temperature to heat and cool buildings.
Advantages of Geothermal Energy:
- Reliable and Sustainable:Geothermal energy is a reliable and sustainable energy source, as the Earth’s heat is constantly replenished.
- Clean and Environmentally Friendly:Geothermal energy does not produce greenhouse gases or air pollutants, making it a clean and sustainable energy source.
- Baseload Power:Geothermal power plants can provide baseload power, meaning they can operate continuously and provide a stable energy supply.
- Multiple Applications:Geothermal energy can be used for electricity generation, space heating, and greenhouse heating.
Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy:
- Limited Geographic Availability:Geothermal resources are not evenly distributed, and only certain areas have suitable geothermal activity.
- High Initial Cost:Geothermal power plants require significant capital investment for drilling and infrastructure.
- Environmental Impacts:Geothermal power plants can have environmental impacts, including emissions of hydrogen sulfide and other gases.
- Potential for Seismic Activity:In some cases, geothermal power plants can trigger minor seismic activity.
Biomass Energy, Energy more sustainable in *
Biomass energy is derived from organic matter, such as wood, crops, and waste, which is burned to generate heat or electricity. Biomass energy is a renewable energy source, as organic matter is constantly replenished through natural processes. Advantages of Biomass Energy:
- Renewable and Sustainable:Biomass energy is a renewable energy source, as organic matter is constantly replenished through natural processes.
- Carbon Neutral:Biomass energy is considered carbon neutral because the carbon dioxide released during combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by the plants during their growth.
- Waste Management:Biomass energy can utilize waste materials, such as agricultural residues and wood waste, reducing landfill waste and promoting waste management.
- Job Creation:The biomass energy industry creates jobs in forestry, agriculture, and energy production.
Disadvantages of Biomass Energy:
- Land Use:Biomass energy production can require significant land areas for growing crops or harvesting wood, raising concerns about land use and deforestation.
- Air Pollution:Burning biomass can release air pollutants, including particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides.
- Efficiency:The efficiency of biomass energy conversion can vary depending on the type of biomass used and the technology employed.
- Sustainability Concerns:Ensuring the sustainable harvesting of biomass is crucial to prevent negative environmental impacts, such as deforestation and soil erosion.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation
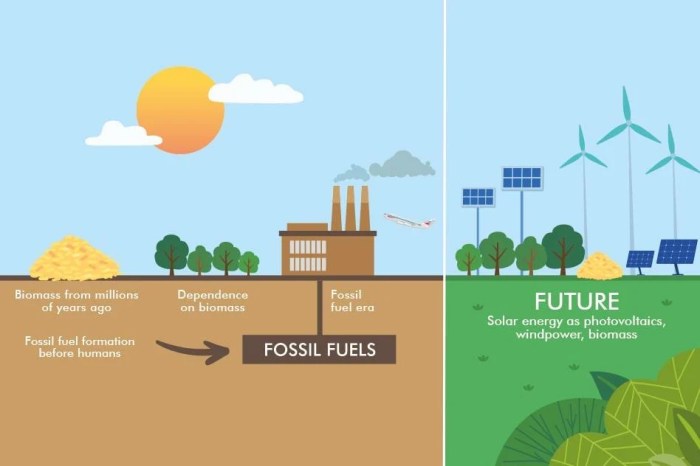
Energy efficiency and conservation are crucial for mitigating climate change and ensuring a sustainable energy future. By reducing energy consumption, we can lessen our reliance on fossil fuels, decrease greenhouse gas emissions, and create a more resilient energy system.
Strategies for Improving Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency strategies aim to reduce energy consumption while maintaining or improving the desired level of service. These strategies can be implemented in various sectors, including homes, businesses, and transportation.
Improving Energy Efficiency in Homes
Homes account for a significant portion of energy consumption. Implementing energy-efficient practices can significantly reduce energy bills and environmental impact.
- Insulation:Proper insulation helps prevent heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling. This can be achieved by adding insulation to attics, walls, and crawl spaces.
- Energy-efficient windows and doors:Double- or triple-paned windows and doors with weatherstripping can significantly reduce heat transfer, improving energy efficiency.
- High-efficiency appliances:Replacing older appliances with Energy Star-rated models can save energy and money. Energy Star appliances are certified to meet strict energy efficiency standards.
- Smart thermostats:Programmable or smart thermostats can automatically adjust temperatures based on occupancy and weather conditions, optimizing heating and cooling schedules.
- LED lighting:LED lights are significantly more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs, reducing energy consumption and lowering electricity bills.
Improving Energy Efficiency in Businesses
Businesses have a significant opportunity to reduce energy consumption and save money by implementing energy-efficient practices.
- Energy audits:Conducting regular energy audits can identify areas where energy waste occurs and recommend improvements.
- Process optimization:Streamlining processes and reducing inefficiencies can significantly reduce energy consumption. This includes optimizing equipment usage, reducing idle time, and improving production processes.
- Building automation systems:Implementing building automation systems can optimize lighting, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning based on occupancy and weather conditions.
- Renewable energy sources:Integrating renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind turbines can reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower energy costs.
- Employee awareness programs:Educating employees about energy-efficient practices can encourage responsible energy consumption in the workplace.
Improving Energy Efficiency in Transportation
Transportation is a major contributor to energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing energy-efficient strategies can reduce fuel consumption and improve air quality.
- Fuel-efficient vehicles:Choosing fuel-efficient vehicles with higher gas mileage can significantly reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
- Electric vehicles:Electric vehicles (EVs) offer zero tailpipe emissions and can be powered by renewable energy sources, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Public transportation:Encouraging the use of public transportation, cycling, and walking can reduce the number of individual vehicles on the road, leading to lower energy consumption and emissions.
- Smart traffic management systems:Implementing smart traffic management systems can optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and fuel consumption.
- Fuel-efficient driving practices:Adopting fuel-efficient driving habits, such as avoiding aggressive acceleration and braking, can improve fuel economy and reduce emissions.
Successful Energy Conservation Programs and Initiatives
Numerous successful energy conservation programs and initiatives have been implemented globally, demonstrating the effectiveness of these efforts in reducing energy consumption and promoting sustainability.
Energy Star Program
The Energy Star program, launched by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, is a voluntary program that certifies products that meet strict energy efficiency standards. By promoting energy-efficient appliances, electronics, and buildings, the Energy Star program has helped reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
“The Energy Star program has saved Americans billions of dollars in energy costs and prevented millions of tons of greenhouse gas emissions.”U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
California’s Energy Efficiency Programs
California has implemented a comprehensive set of energy efficiency programs, including appliance standards, building codes, and rebates for energy-efficient products. These programs have significantly reduced energy consumption and helped California achieve its ambitious climate goals.
“California’s energy efficiency programs have saved consumers billions of dollars and reduced greenhouse gas emissions by millions of metric tons.”
California Energy Commission
Green Building Standards
Green building standards, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), promote sustainable design and construction practices, including energy efficiency. Buildings certified under these standards typically consume less energy and have a lower environmental impact.
“Green buildings can reduce energy consumption by up to 50% and water consumption by up to 40% compared to conventional buildings.”U.S. Green Building Council
The Role of Behavioral Change and Public Awareness
Behavioral change and public awareness are crucial for promoting energy efficiency and conservation. By educating the public about the benefits of energy efficiency and providing incentives for adopting energy-saving practices, we can encourage widespread adoption of these practices.
Public Education Campaigns
Public education campaigns can raise awareness about the importance of energy efficiency and conservation, provide practical tips for saving energy, and highlight the benefits of adopting energy-efficient practices. These campaigns can use various media platforms, including television, radio, social media, and public events.
Incentives and Rebates
Governments and utility companies can offer financial incentives and rebates to encourage consumers to adopt energy-efficient technologies and practices. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates for energy-efficient appliances, and subsidies for renewable energy systems.
Energy Efficiency Standards
Implementing energy efficiency standards for appliances, buildings, and vehicles can ensure that products meet minimum energy efficiency requirements. These standards can help drive innovation in energy-efficient technologies and encourage manufacturers to produce more efficient products.
Community Engagement
Engaging communities in energy efficiency initiatives can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility for reducing energy consumption. This can involve community-based energy audits, energy-saving contests, and collaborative efforts to promote energy efficiency practices.
Policy and Regulation
The transition to a sustainable energy future requires a multifaceted approach, with government policies and regulations playing a pivotal role in shaping the energy landscape. By setting targets, providing incentives, and establishing regulatory frameworks, governments can encourage innovation, investment, and widespread adoption of sustainable energy technologies.
Carbon Pricing Mechanisms
Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems, are designed to internalize the environmental costs associated with carbon emissions. Carbon taxes directly impose a price on carbon emissions, while cap-and-trade systems establish a limit on emissions and allow companies to trade permits to emit carbon.
These mechanisms incentivize businesses and individuals to reduce their carbon footprint by making polluting activities more expensive.
“Carbon pricing mechanisms have proven effective in reducing emissions and promoting cleaner energy sources in various countries.”
Renewable Energy Mandates
Renewable energy mandates require utilities or energy producers to generate a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower. These mandates stimulate investment in renewable energy infrastructure, create jobs in the renewable energy sector, and accelerate the transition to a cleaner energy system.
Energy Efficiency Standards
Energy efficiency standards set minimum performance requirements for appliances, buildings, and other energy-consuming products. By promoting the use of energy-efficient technologies, these standards reduce energy consumption, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and save consumers money on their energy bills.
Challenges and Opportunities
Implementing sustainable energy policies presents both challenges and opportunities. One challenge is balancing the need for energy security with the transition to renewable energy sources. Another challenge is ensuring equitable access to sustainable energy technologies, particularly in developing countries. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation, economic growth, and improved public health.
The Future of Sustainable Energy: Energy More Sustainable In *
The future of energy is bright, driven by a confluence of technological advancements, policy shifts, and a growing global awareness of the urgent need to transition to a sustainable energy system. This transition promises a future powered by clean, efficient, and reliable energy sources, offering significant benefits for both the environment and the economy.
Key Trends and Innovations
The future of sustainable energy is being shaped by a number of key trends and innovations.
- Renewable Energy Growth:The cost of renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, has plummeted in recent years, making them increasingly competitive with fossil fuels. This trend is expected to continue, driving further adoption of renewable energy sources around the world.
- Energy Storage Advancements:Energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro, are crucial for integrating intermittent renewable energy sources into the grid. Advancements in these technologies are making energy storage more efficient, affordable, and scalable, paving the way for a more reliable and resilient energy system.
- Smart Grid Technologies:Smart grid technologies are enabling better monitoring, control, and optimization of the electricity grid. This allows for more efficient integration of renewable energy sources, improved grid reliability, and enhanced energy efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:AI and ML are being increasingly used in the energy sector for tasks such as predicting energy demand, optimizing energy consumption, and improving the performance of renewable energy systems.
These technologies are expected to play a significant role in driving further innovation and efficiency in the sustainable energy sector.
- Hydrogen Energy:Hydrogen is a clean and versatile energy carrier that can be produced from renewable sources. Advancements in hydrogen production, storage, and distribution technologies are making hydrogen energy a more viable option for transportation, heating, and industrial applications.
Impact of Technological Advancements and Policy Changes
Technological advancements and policy changes are poised to significantly impact the energy sector, accelerating the transition to a sustainable energy future.
- Declining Costs of Renewable Energy:The continued decline in the cost of renewable energy technologies will make them increasingly attractive to consumers and businesses, driving further adoption and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. For example, the cost of solar photovoltaic (PV) panels has fallen by over 80% since 2010, making solar energy a cost-effective option in many regions.
- Government Incentives and Regulations:Governments around the world are implementing policies to promote renewable energy and energy efficiency, such as tax incentives, subsidies, and renewable energy mandates. These policies are creating a favorable environment for the development and deployment of sustainable energy technologies. For instance, the United States’ Inflation Reduction Act includes significant investments in renewable energy, clean transportation, and energy efficiency, aiming to accelerate the transition to a clean energy economy.
- Carbon Pricing Mechanisms:Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes and emissions trading schemes, are being implemented to incentivize businesses and individuals to reduce their carbon footprint. These mechanisms can help drive investment in clean energy technologies and accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy.
The Role of Collaboration and Innovation
Collaboration and innovation are crucial for achieving a sustainable energy future.
- Public-Private Partnerships:Collaboration between governments, businesses, and research institutions is essential for developing and deploying sustainable energy technologies. Public-private partnerships can leverage the strengths of each sector to accelerate innovation, reduce costs, and overcome regulatory hurdles.
- Open Innovation and Knowledge Sharing:Open innovation and knowledge sharing are critical for fostering a collaborative ecosystem in the sustainable energy sector.
Sharing research findings, best practices, and technological advancements can accelerate the development and deployment of clean energy solutions.
- International Cooperation:International cooperation is essential for addressing the global challenges of climate change and energy security. Collaborative efforts can facilitate technology transfer, promote investment in clean energy, and ensure a just and equitable transition to a sustainable energy future.