Startups fight to ban destroy pfas forever chemicals with tech – Startups Fight to Ban “Forever Chemicals” with Tech: In the face of a growing crisis, a new generation of companies is rising to combat the threat of PFAS, also known as “forever chemicals.” These persistent, man-made chemicals have infiltrated our water, food, and even our bodies, posing significant risks to human health and the environment.
Driven by a commitment to a healthier future, these startups are developing innovative solutions to detect, remove, and ultimately prevent the spread of these dangerous compounds.
The fight against PFAS is a multi-faceted battle that requires a collaborative approach. Startups are spearheading the charge by creating PFAS-free alternatives for various applications, while others are pioneering cutting-edge technologies to detect and remove PFAS from contaminated sources. Their efforts are bolstered by advocacy groups pushing for stricter regulations and legislation to limit the production and use of these chemicals.
The PFAS Crisis
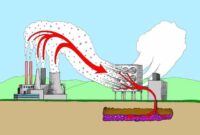
The PFAS crisis is a growing threat to human health and the environment. These “forever chemicals” are a group of synthetic chemicals that have been used in a wide range of products for decades. They are highly persistent and resistant to breakdown, meaning they can remain in the environment and our bodies for a very long time.
History and Discovery of PFAS Chemicals
PFAS chemicals were first synthesized in the 1930s and have been used in a variety of products, including non-stick cookware, firefighting foam, food packaging, and clothing. Their unique properties, such as their ability to repel water, oil, and grease, made them highly desirable for many applications.
Environmental and Health Risks of PFAS Exposure
PFAS chemicals have been linked to a range of health problems, including:
- Immune system deficiencies
- Hormonal disruptions
- Liver cancer
- Kidney cancer
- Testicular cancer
- High cholesterol
- Pregnant women may experience low birth weight and preterm delivery
These chemicals can also accumulate in the environment, contaminating water, soil, and air. They have been found in drinking water, food, and even in human blood.
Real-World Examples of PFAS Contamination and Its Impact on Communities, Startups fight to ban destroy pfas forever chemicals with tech
PFAS contamination has been documented in numerous locations around the world, with significant impacts on communities.
Discover more by delving into europes homegrown battery cells could end reliance on china by further.
- PFOA contamination in Parkersburg, West Virginia: DuPont, a major manufacturer of PFOA, discharged the chemical into the Ohio River for decades. This resulted in widespread contamination of the river and the surrounding communities, leading to health problems and legal battles.
- PFAS contamination in Fayetteville, North Carolina: The city’s drinking water supply was contaminated with PFAS chemicals from a nearby military base. This resulted in a public health emergency and a major cleanup effort.
- PFAS contamination in Michigan: The state has been dealing with widespread PFAS contamination, particularly in the Great Lakes region. This contamination has affected drinking water, fish, and wildlife, and has raised concerns about the health of residents.
The Fight Against PFAS
The fight against PFAS is a multifaceted challenge that requires a concerted effort from governments, industries, and research institutions. While regulations and clean-up efforts are crucial, innovative technologies and alternative materials are playing a vital role in reducing PFAS contamination and preventing its further spread.
PFAS-Free Alternatives
Startups are leading the charge in developing PFAS-free alternatives for a wide range of applications. These alternatives aim to replicate the desired properties of PFAS while avoiding the associated environmental and health risks.
- Fluoropolymer Alternatives:Companies are developing PFAS-free alternatives to fluoropolymers, which are commonly used in non-stick cookware, textiles, and other products. These alternatives include materials like silicone, ceramic, and bio-based polymers that offer similar properties without the harmful effects of PFAS.
- Fire Retardants:Startups are exploring new fire retardant materials that do not rely on PFAS. These include using mineral-based compounds, intumescent coatings, and bio-based fire retardants, which provide effective fire protection without the risks associated with PFAS.
- Water Repellents:Several companies are developing PFAS-free water repellents for textiles and other applications. These alternatives include using modified silicones, fluorinated polymers without PFAS, and bio-based materials that provide durable water resistance without the environmental impact of PFAS.
Innovative Technologies for PFAS Detection and Removal
Emerging technologies are being deployed to detect and remove PFAS from contaminated sources. These technologies offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact.
- Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs):AOPs use powerful oxidants like ozone, hydrogen peroxide, and UV light to break down PFAS molecules into less harmful substances. This technology is particularly effective for treating contaminated water and wastewater.
- Activated Carbon Adsorption:Activated carbon is a highly porous material that can effectively adsorb PFAS from water and soil. However, the effectiveness of activated carbon depends on the specific type of PFAS and the conditions of the contaminated site.
- Bioaugmentation:This method involves introducing microorganisms to contaminated sites that can break down PFAS molecules. Bioaugmentation can be a cost-effective and environmentally friendly approach, but it requires careful selection of microorganisms and optimization of the treatment process.
Comparing PFAS Remediation Methods
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) | Highly effective in breaking down PFAS molecules, versatile for treating various sources of contamination. | Can be expensive, requires specialized equipment, and may produce byproducts that need further treatment. |
| Activated Carbon Adsorption | Cost-effective, widely available, and effective for removing a range of PFAS compounds. | Requires regular replacement of carbon, can be less effective for certain PFAS, and may not completely remove all PFAS. |
| Bioaugmentation | Environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and can be used in situ. | Requires careful selection of microorganisms, can be time-consuming, and may not be effective for all types of PFAS. |
| PFAS-Free Alternatives | Eliminates the use of PFAS, promotes sustainable practices, and reduces environmental and health risks. | May require significant investment in research and development, and the availability of alternatives may vary depending on the application. |
The Role of Regulation and Legislation

The global community is increasingly recognizing the urgency of addressing the PFAS crisis. Regulation and legislation play a crucial role in mitigating the risks associated with these persistent chemicals.
The Current Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for PFAS varies significantly across countries. Some countries have adopted comprehensive regulations, while others are still in the early stages of developing their regulatory frameworks. Here is a brief overview:
- United States:The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set health advisories for PFAS in drinking water, but has not yet established enforceable standards. Several states, however, have implemented their own regulations, including maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) for PFAS in drinking water.
The EPA is also developing a comprehensive PFAS strategy that includes regulations, guidance, and research initiatives.
- European Union:The EU has adopted a number of regulations and directives related to PFAS, including restrictions on the use of certain PFAS in consumer products. The EU is also working on a proposal for a comprehensive PFAS strategy, which would include a ban on the production and use of certain PFAS and a phase-out of other PFAS.
- Canada:Canada has set guidelines for PFAS in drinking water, but has not yet established enforceable standards. The Canadian government is also working on a national PFAS strategy.
- Australia:Australia has established a number of regulations related to PFAS, including restrictions on the use of certain PFAS in firefighting foam. The Australian government is also working on a national PFAS management plan.
Challenges in Regulating PFAS
Regulating PFAS presents several challenges due to their widespread use and persistence:
- Widespread Use:PFAS are used in a wide range of products, including non-stick cookware, food packaging, firefighting foam, and textiles. This widespread use makes it difficult to regulate PFAS without significantly impacting industries and consumers.
- Persistence:PFAS are very persistent in the environment and can remain in the environment for many years. This persistence makes it difficult to remediate PFAS contamination and can lead to long-term exposure to these chemicals.
- Complexity:There are thousands of different PFAS chemicals, each with its own unique properties and potential risks. This complexity makes it challenging to develop effective regulations that address all PFAS.
- Data Gaps:There are still significant data gaps regarding the health effects of many PFAS. This lack of data makes it difficult to set appropriate regulatory limits.
The Role of Advocacy Groups
Advocacy groups play a critical role in pushing for stricter regulations and policies on PFAS. These groups often conduct research, raise public awareness, and lobby government officials to take action. Examples of advocacy groups working on PFAS include:
- Environmental Defense Fund (EDF):EDF is a non-profit organization that works to protect the environment. EDF has been a leading voice in the fight to regulate PFAS.
- Center for Environmental Health (CEH):CEH is a non-profit organization that works to protect human health from toxic chemicals. CEH has been active in advocating for PFAS regulations.
- Sierra Club:The Sierra Club is a grassroots environmental organization that advocates for protecting the environment. The Sierra Club has been involved in efforts to address PFAS contamination.
The Future of PFAS: Startups Fight To Ban Destroy Pfas Forever Chemicals With Tech

The fight against PFAS is far from over. While significant progress has been made in raising awareness and implementing regulations, the challenge of eliminating these persistent chemicals from our environment and bodies remains a formidable task. The future of PFAS hinges on a multi-pronged approach that focuses on preventing contamination, promoting responsible alternatives, and fostering innovation.
Preventing Future Contamination
Preventing PFAS contamination in the first place is crucial to safeguarding human health and the environment. This requires a comprehensive strategy that addresses the sources of PFAS release and promotes the use of safer alternatives.
- Phase out PFAS in Consumer Products:Implementing bans and restrictions on PFAS in non-essential consumer products, such as non-stick cookware, food packaging, and textiles, can significantly reduce the amount of PFAS entering the environment and our bodies.
- Promote Safer Alternatives:Encouraging the development and adoption of PFAS-free alternatives in industrial and consumer applications is vital. This requires investments in research and development, as well as incentives for companies to transition to safer products.
- Improve Waste Management Practices:Implementing proper waste management practices, including the disposal and treatment of PFAS-containing materials, is essential to prevent PFAS from leaching into the environment. This involves establishing regulations for the disposal of PFAS-contaminated waste and promoting the development of technologies for treating and destroying PFAS.
- Strengthen Industrial Regulations:Enhancing regulations for industrial processes that use or produce PFAS is critical to minimize releases into the environment. This includes setting emission limits, requiring best available technologies, and promoting responsible waste management practices.