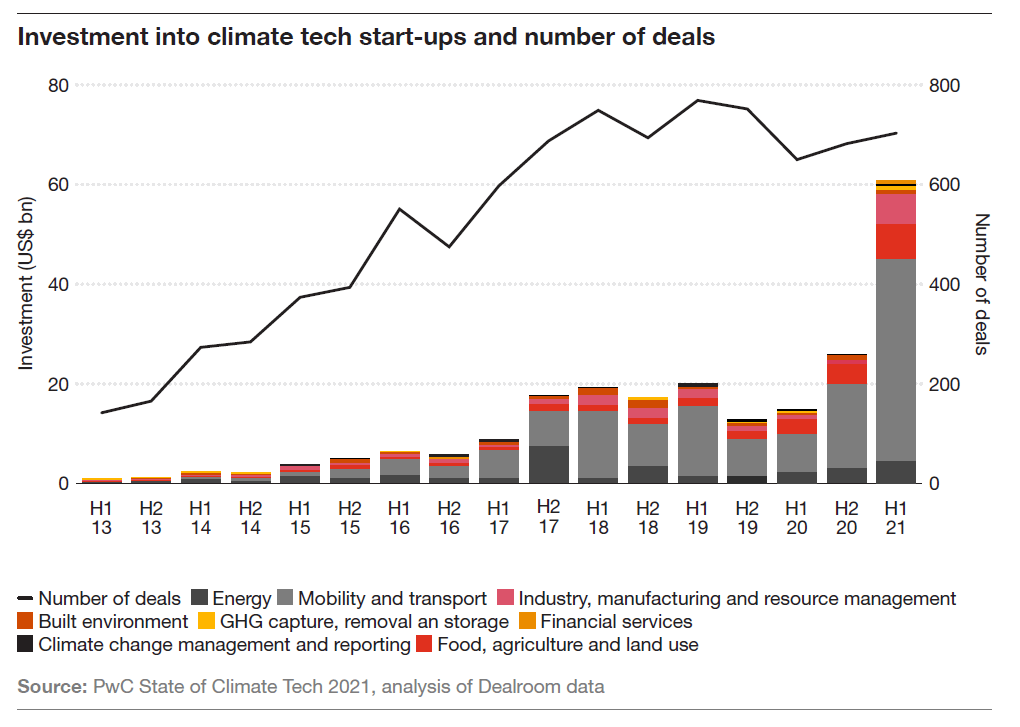
Climate tech eqt venture capital startups investment is booming, reflecting a growing urgency to address climate change. Investors are pouring money into innovative solutions that tackle everything from renewable energy to carbon capture. This surge in investment is fueled by a combination of factors, including the increasing severity of climate change, the emergence of promising new technologies, and the growing awareness of the economic potential of the climate tech sector.
From startups developing cutting-edge solar panels to those pioneering carbon sequestration methods, the climate tech landscape is diverse and dynamic. These companies are not only working to mitigate climate change, but they are also creating new industries and jobs. The journey of climate tech investment is filled with challenges and opportunities, and this blog explores the key players, strategies, and future prospects of this exciting sector.
The Rise of Climate Tech
The climate crisis is a pressing global issue, and technological innovation is crucial in mitigating its impacts. Climate tech, a burgeoning sector focused on developing solutions to address climate change, is gaining momentum and attracting significant investment.
The Importance of Climate Tech
Climate tech plays a pivotal role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and adapting to the changing climate. The sector encompasses a wide range of technologies, including renewable energy generation, energy storage, carbon capture and storage, sustainable agriculture, and climate-resilient infrastructure.
Key Challenges and Opportunities
The climate tech sector faces numerous challenges, including the need for large-scale deployment, regulatory hurdles, and securing adequate funding. However, the sector also presents significant opportunities for innovation and growth.
Challenges
- Scale and Deployment:Climate tech solutions require widespread adoption and deployment to have a meaningful impact on global emissions. Scaling up these technologies can be challenging due to infrastructure limitations, cost considerations, and logistical complexities.
- Regulatory Frameworks:The development and deployment of climate tech often require clear and supportive regulatory frameworks. Lack of consistent policies and regulations can create uncertainty and hinder innovation.
- Funding and Investment:Climate tech companies need substantial funding to develop, test, and deploy their solutions. Attracting investment can be difficult, especially for early-stage startups.
Opportunities
- Technological Advancements:Ongoing advancements in technology are driving innovation in climate tech. New materials, energy storage solutions, and artificial intelligence are creating exciting opportunities for tackling climate change.
- Growing Investor Interest:Investors are increasingly recognizing the potential of climate tech to generate both financial returns and positive social impact. Venture capital firms, corporations, and governments are allocating significant resources to climate tech startups.
- Policy Support:Governments around the world are enacting policies to incentivize the adoption of climate tech solutions. This includes tax credits, subsidies, and regulatory frameworks that support renewable energy and sustainable practices.
Examples of Groundbreaking Climate Tech Solutions
Numerous innovative climate tech solutions are emerging, addressing various aspects of climate change.
Renewable Energy
- Solar Power:Advancements in solar panel efficiency and cost reduction have made solar power a competitive source of energy. Large-scale solar farms and rooftop solar installations are contributing to a significant reduction in carbon emissions.
- Wind Power:Offshore wind farms are generating clean energy on a massive scale. Technological advancements in wind turbine design and efficiency have increased the capacity and reliability of wind power.
- Geothermal Energy:Geothermal power plants utilize heat from the Earth’s interior to generate electricity. This renewable energy source is reliable and emissions-free, but its deployment is limited by geographical constraints.
Energy Storage
- Lithium-ion Batteries:These batteries are widely used in electric vehicles and grid-scale energy storage systems. Ongoing research is focused on improving battery performance, reducing costs, and developing alternative battery chemistries.
- Flow Batteries:Flow batteries offer long-duration energy storage capabilities, suitable for grid-scale applications. They are particularly useful for balancing intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
Carbon Capture and Storage
- Direct Air Capture:This technology removes carbon dioxide directly from the atmosphere. While still in its early stages of development, direct air capture holds the potential to mitigate existing carbon emissions.
- Carbon Sequestration:This involves storing captured carbon dioxide underground or in other geological formations. Carbon sequestration can help reduce atmospheric carbon dioxide levels and mitigate climate change.
Venture Capital’s Role in Climate Tech: Climate Tech Eqt Venture Capital Startups Investment
The climate tech sector has witnessed a surge in venture capital investment, reflecting the growing awareness of the urgency to address climate change and the potential of innovative solutions. Venture capitalists (VCs) are playing a crucial role in fostering the development and scaling of climate tech startups, recognizing the significant financial and societal returns that can be generated.
Factors Driving VC Investment in Climate Tech
The increasing interest of VCs in climate tech is driven by a confluence of factors, including:
- Growing Investor Interest in ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) Investing:Investors are increasingly seeking to align their investments with their values, and climate tech offers a compelling opportunity to contribute to a more sustainable future. This has led to a rise in ESG-focused funds and a greater emphasis on sustainability considerations in investment decisions.
- Government Policies and Regulations:Governments worldwide are implementing policies and regulations aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting clean energy technologies. These policies create a favorable environment for climate tech startups, increasing their market potential and attractiveness to investors.
- Technological Advancements:The rapid pace of technological innovation in areas such as renewable energy, energy storage, and carbon capture has created new opportunities for climate tech startups. VCs are eager to invest in these technologies, recognizing their potential to disrupt traditional industries and drive significant economic growth.
- Growing Awareness of Climate Change Risks:The increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and other climate-related risks have raised awareness of the urgency to address climate change. This has led to greater demand for climate solutions, driving investment in climate tech startups.
Check what professionals state about 3 ways data center design will change in the future and its benefits for the industry.
Areas of Climate Tech Attracting VC Funding
VC funding in climate tech is concentrated in several key areas:
- Renewable Energy:This sector includes technologies such as solar, wind, and hydropower, as well as advanced energy storage solutions. VCs are investing heavily in startups developing innovative and cost-effective renewable energy technologies to replace fossil fuels.
- Electric Vehicles and Mobility:The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is a major focus for climate tech investors. VCs are funding startups developing EV infrastructure, battery technology, and autonomous driving systems.
- Carbon Capture and Storage:This sector involves technologies that capture and store carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes and power plants. VCs are investing in startups developing innovative carbon capture and storage solutions to mitigate climate change.
- Sustainable Agriculture:Climate tech investors are also supporting startups developing sustainable agricultural practices, such as precision farming, vertical farming, and alternative protein sources. These technologies aim to reduce the environmental impact of agriculture while improving food security.
- Climate Adaptation:As the effects of climate change become more pronounced, VCs are investing in startups developing solutions to adapt to these changes. This includes technologies for water management, flood control, and drought mitigation.
Climate Tech Startups
The climate tech landscape is teeming with innovation, with startups tackling climate change from diverse angles. These companies are developing groundbreaking solutions across various sectors, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in renewable energy, carbon capture, sustainable agriculture, and more.
Categories of Climate Tech Startups
Climate tech startups can be categorized based on their focus areas, reflecting the wide range of challenges they address. These categories include:
- Renewable Energy: Companies in this category develop and deploy technologies to generate clean energy from sources like solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal. Examples include:
- SolarEdge: A global leader in smart energy technology, providing solar inverters and power optimizers for residential and commercial solar installations.
- Vestas: A leading wind turbine manufacturer, supplying turbines for onshore and offshore wind farms worldwide.
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Startups in this category focus on capturing and storing carbon dioxide emissions from various sources, preventing them from entering the atmosphere. Examples include:
- Global Thermostat: A company developing technology to capture carbon dioxide from industrial sources, converting it into valuable products.
- Carbon Engineering: A company focused on capturing carbon dioxide directly from the air using a large-scale direct air capture technology.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Startups in this category aim to improve agricultural practices, reduce environmental impact, and increase food production efficiency. Examples include:
- Indigo Agriculture: A company developing microbial solutions to improve crop yields, reduce fertilizer use, and enhance soil health.
- Plenty: A company building vertical farms that use technology to grow fresh produce indoors, reducing water usage and land footprint.
- Climate Adaptation: Startups in this category focus on developing solutions to adapt to the impacts of climate change, such as rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and water scarcity. Examples include:
- Climate Corporation: A company providing farmers with data-driven insights and tools to manage risk and improve farm productivity in the face of climate change.
- The Climate Corporation: A company providing farmers with data-driven insights and tools to manage risk and improve farm productivity in the face of climate change.
Challenges and Opportunities
Climate tech startups face unique challenges and opportunities:
- Funding: Securing funding is crucial for startups, especially in the early stages. While interest in climate tech is growing, securing investment can still be challenging, especially compared to other sectors.
- Regulation: Climate tech startups often operate in rapidly evolving regulatory landscapes, requiring them to navigate complex and sometimes unclear rules and policies.
- Market Adoption: Scaling up and achieving market adoption can be a significant hurdle, as climate tech solutions often require a shift in consumer behavior or industry practices.
- Technological Advancement: The field of climate tech is constantly evolving, requiring startups to continuously innovate and adapt to stay ahead of the curve.
Investment Strategies for Climate Tech
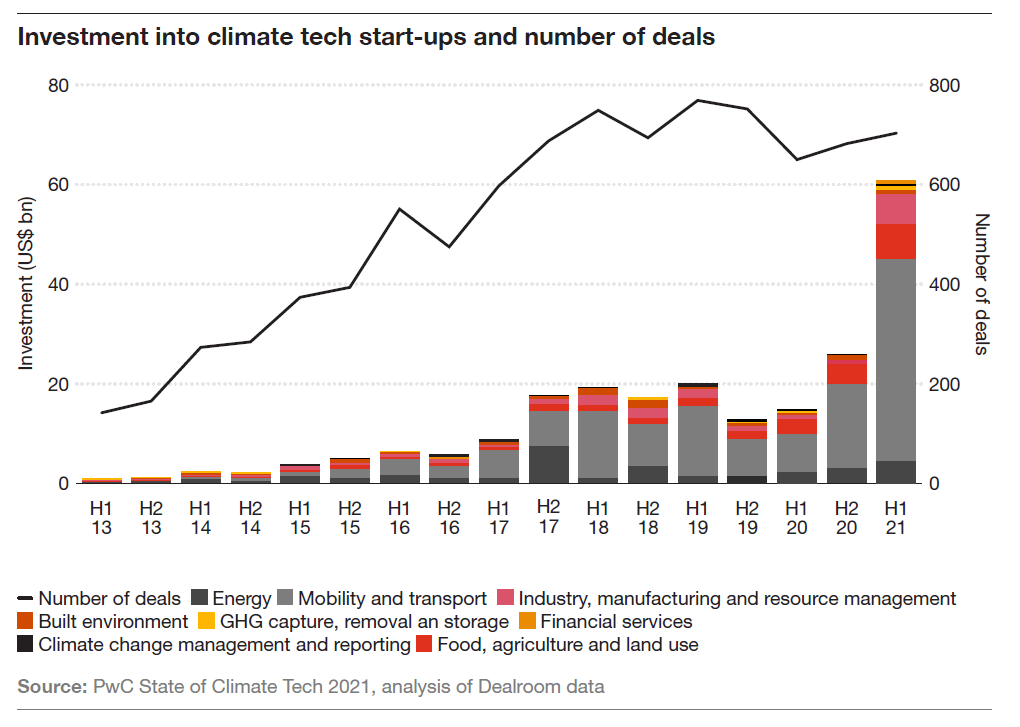
Venture capitalists (VCs) are increasingly investing in climate tech, recognizing the significant potential for both financial returns and positive societal impact. Their investment strategies vary depending on the stage of the startup, the specific technology, and the VC’s own risk appetite.
Investment Strategies in Climate Tech
VCs employ a range of strategies to invest in climate tech startups, often tailoring their approach to the specific sector and stage of development. Here are some common strategies:
- Early-Stage Investment:VCs often invest in seed-stage companies developing innovative solutions with high growth potential. These investments are typically smaller but offer the potential for significant returns if the company succeeds.
- Growth-Stage Investment:VCs invest in companies that have already proven their technology and are scaling their operations. These investments are typically larger and involve more due diligence.
- Series A and B Funding:VCs play a crucial role in funding early-stage startups, providing capital for product development, team expansion, and market validation. They often lead these funding rounds and actively engage with the startup’s management team.
- Later-Stage Funding:VCs participate in later-stage funding rounds, providing capital for expansion, acquisitions, and market domination. They often have a more strategic role, leveraging their network and expertise to support the startup’s growth.
- Impact Investing:VCs increasingly focus on impact investing, seeking investments that generate both financial returns and positive social or environmental impact. This approach aligns with the goals of climate tech, where solutions aim to mitigate climate change and create a more sustainable future.
Risk and Reward Profiles
Climate tech investments come with both significant risks and rewards. Understanding these factors is crucial for VCs to make informed decisions:
- High Growth Potential:Climate tech startups often address large and growing markets, presenting opportunities for substantial growth. For example, the global renewable energy market is expected to reach \$2.1 trillion by 2025, according to a report by the International Energy Agency.
- Technological Uncertainty:Climate tech startups often develop new technologies, which may face challenges in scaling, adoption, and regulatory approval. VCs need to assess the technology’s maturity, feasibility, and potential for commercialization.
- Market Volatility:The climate tech market can be influenced by factors such as government policies, energy prices, and consumer preferences, creating volatility and uncertainty for investors. VCs need to consider the market dynamics and potential risks associated with these factors.
- Long-Term Investment Horizon:Climate tech startups typically require a longer investment horizon than traditional technology companies, as they may take time to develop and scale their solutions. VCs need to be patient and willing to support the startup’s long-term growth.
- Positive Societal Impact:Climate tech investments offer the potential for significant positive societal impact by contributing to a more sustainable future. This aspect can be a key motivator for impact-driven investors, who seek to align their investments with their values.
Due Diligence for Climate Tech Startups
VCs conduct thorough due diligence before investing in climate tech startups, evaluating various aspects:
- Technology Assessment:VCs evaluate the technology’s novelty, feasibility, and potential for commercialization. They may consult with experts in the field and conduct technical due diligence to assess the technology’s viability and potential for disruption.
- Market Analysis:VCs analyze the market size, growth potential, and competitive landscape. They assess the startup’s target market, its competitive advantages, and its ability to capture market share.
- Team Evaluation:VCs assess the team’s experience, expertise, and passion for solving the climate crisis. They look for a strong management team with a proven track record and a deep understanding of the industry.
- Financial Projections:VCs analyze the startup’s financial projections, including revenue forecasts, cost structure, and profitability. They assess the company’s financial health and its ability to generate sustainable returns on investment.
- Regulatory and Legal Compliance:VCs evaluate the startup’s compliance with relevant regulations and laws, particularly those related to environmental protection and sustainability. They may consult with legal experts to assess the startup’s legal framework and potential risks.
Impact and Future of Climate Tech
Climate tech solutions have the potential to significantly impact the fight against climate change. By developing innovative technologies and approaches, these companies can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve resource efficiency, and build resilience against climate change impacts.
Potential Impact of Climate Tech Solutions, Climate tech eqt venture capital startups investment
Climate tech solutions can significantly contribute to mitigating climate change by addressing key areas like:
- Renewable Energy:Developing and deploying renewable energy technologies, such as solar, wind, and geothermal, can reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease carbon emissions. For example, companies like Tesla and Sunrun are leading the charge in solar energy deployment, contributing to a cleaner energy future.
- Energy Efficiency:Implementing energy-efficient technologies and practices in buildings, transportation, and industrial processes can significantly reduce energy consumption and associated emissions. Companies like Johnson Controls and Siemens are actively developing and implementing smart building technologies that optimize energy usage.
- Carbon Capture and Storage:Technologies that capture and store carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes and power plants can help reduce the amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere. Companies like Global Thermostat and Climeworks are pioneering carbon capture technologies.
- Sustainable Agriculture:Developing sustainable farming practices, such as precision agriculture and regenerative agriculture, can help reduce emissions from agriculture and improve food security. Companies like Indigo Ag and Climate Corporation are using data and technology to optimize crop yields and reduce environmental impact.
- Climate Adaptation:Implementing climate adaptation strategies, such as drought-resistant crops and flood-resistant infrastructure, can help communities prepare for and mitigate the impacts of climate change. Companies like FloodFlash and Resilience Labs are developing innovative solutions to address these challenges.
Future Trends and Challenges in Climate Tech
The climate tech sector is rapidly evolving, with several key trends and challenges shaping its future:
- Increased Investment:Venture capital and other forms of investment in climate tech are expected to continue to grow significantly in the coming years. As the urgency to address climate change increases, investors are increasingly seeking opportunities to support climate-friendly technologies and businesses.
- Focus on Climate Resilience:Beyond reducing emissions, there is a growing focus on building resilience to climate change impacts, such as extreme weather events and rising sea levels. This includes developing technologies and strategies to adapt to these changes and minimize their negative effects.
- Technological Convergence:We are witnessing a convergence of technologies in the climate tech space, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things. These technologies are being combined to develop more efficient and effective solutions for climate change mitigation and adaptation.
- Policy and Regulatory Support:Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in driving climate tech innovation and deployment. Policies that incentivize clean energy, carbon pricing, and sustainable practices can accelerate the adoption of climate-friendly technologies.
- Scaling and Deployment:A significant challenge for climate tech is scaling up and deploying solutions at a large enough scale to have a meaningful impact on climate change. This requires collaboration between startups, established companies, governments, and other stakeholders.
Key Players, Investments, and Expected Outcomes
The following table provides an overview of key players, investments, and expected outcomes in the climate tech space: