Unrealistic Job Offers: 5 Ways To Identify Job Phishing Schemes
5 ways to identify job phishing schemes – Phishing schemes often try to lure victims with promises of lucrative opportunities that seem too good to be true. These unrealistic job offers are designed to catch your attention and make you less cautious about verifying the legitimacy of the offer.Unrealistic job offers often come with red flags that can help you identify them.
By being aware of these red flags, you can protect yourself from falling victim to a phishing scheme.
Examples of Unrealistic Job Offers
Unrealistic job offers often include promises of extremely high salaries, minimal work requirements, and work-from-home positions that require little to no experience. Here are some examples of unrealistic job titles or descriptions that could indicate a phishing scheme:
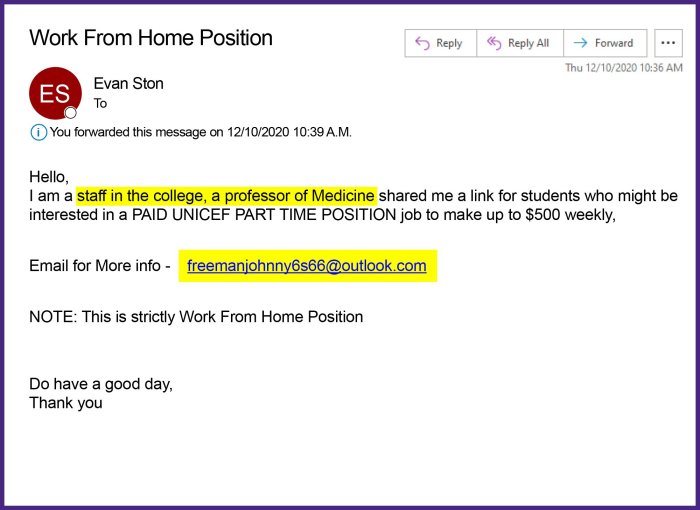
- “Work from home, earn $10,000 per week!”This type of offer often involves simple tasks, like data entry or online surveys, and promises high earnings for minimal effort.
- “No experience needed, become a virtual assistant!”Many legitimate virtual assistant positions require specific skills and experience.
- “High-paying executive position, no qualifications required.”This type of offer is highly unlikely and should be treated with suspicion.
Language Used in Unrealistic Job Offers
Legitimate job offers use clear and concise language that accurately describes the job responsibilities and qualifications required. In contrast, phishing schemes often use vague and overly enthusiastic language to entice victims. Here are some examples of the language used in phishing schemes:
“This is a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity!”
“Make easy money from home!”
“No experience required, we will train you!”
In contrast, legitimate job offers typically use language that is more specific and focused on the job requirements:
“This position requires 3+ years of experience in customer service.”
“Responsibilities include data entry and customer support.”
Discover how stanford ai experts dispute claims google lamda language model is sentient has transformed methods in this topic.
“Qualifications include a bachelor’s degree in business administration.”
Request for Personal Information
Phishing schemes often attempt to trick job seekers into providing sensitive personal information. This tactic can be used to steal identities, access bank accounts, or even commit fraud. Understanding the types of information that should never be shared during the job application process is crucial in protecting yourself from such scams.
Types of Personal Information to Avoid Sharing
Legitimate employers will never ask for certain types of personal information during the application process. This includes:
- Social Security Number (SSN):Your SSN is a highly sensitive piece of information that should only be provided to trusted entities, like the government or your employer after you have been officially hired. Sharing it during the application process is a major red flag.
- Bank Account Details:Legitimate employers will not ask for your bank account information during the application process. This information is only required once you have been hired and are ready to receive your salary.
- Passport or Driver’s License Number:While these documents may be required for background checks after you have been hired, they should never be requested during the initial application process.
- Credit Card Information:Legitimate employers will never ask for your credit card information.
- Medical Information:Providing your medical history or information related to disabilities is generally not required during the application process. Employers are legally prohibited from asking for this information unless it is directly related to the job requirements.
Why Phishing Schemes Request Personal Information
Phishing schemes request personal information to exploit job seekers. They can use this information to:
- Steal Identities:Phishing schemes often collect personal information to create fake identities, which they can use to open credit cards, apply for loans, or commit other forms of fraud.
- Access Bank Accounts:By obtaining bank account details, phishers can access your funds and drain your accounts.
- Engage in Other Forms of Fraud:Phishers may use the collected information to engage in other forms of fraud, such as impersonating you or selling your data on the dark web.
Legitimate vs. Phishing Requests
It is important to be able to distinguish between legitimate requests for information and phishing attempts. Here’s a table highlighting the key differences:
| Legitimate Request | Phishing Request |
|---|---|
| Requests for basic information like your name, contact details, and work experience. | Asks for sensitive information like your SSN, bank account details, or passport number. |
| Provides clear and concise communication about the job requirements and the application process. | Uses vague or confusing language and may pressure you to provide information quickly. |
| Uses professional email addresses and official company websites. | Uses unprofessional or suspicious email addresses and websites that may look like official company websites but are not. |
| Asks for information through secure channels like official company websites or reputable job boards. | Asks for information through unsecured channels like personal email accounts or third-party websites. |
Suspicious Links and Websites

Phishing emails often contain links that lead to fake websites designed to steal your personal information. Learning to spot these suspicious links is crucial in protecting yourself from falling victim to a phishing scheme.
Identifying Suspicious Links and Websites
It is important to carefully examine the links and websites you encounter, especially when they appear in unsolicited emails or messages. Here are some key indicators of a suspicious link or website:
- Misspellings in URLs:Phishing websites often intentionally misspell the name of a legitimate company in the URL. For example, instead of “amazon.com,” they might use “amaz0n.com” or “amzon.com.”
- Unfamiliar Domains:Pay close attention to the domain name (the part after the “www.” or “http://”). If the domain name looks unfamiliar or doesn’t match the company you expect, it’s a red flag. For instance, if you receive an email claiming to be from Apple, but the link leads to a website with a domain like “apple-support.net,” it’s likely a phishing attempt.
- Generic or Unrelated Domain Names:Phishing websites sometimes use generic domain names like “login.com” or “secure-account.net” that could be associated with various companies. This lack of specificity should raise suspicion.
- Suspicious URL Shorteners:Links shortened using services like Bitly or TinyURL can be difficult to assess for legitimacy. While legitimate websites might use URL shorteners, it’s best to exercise caution when clicking on shortened links, especially if you’re unsure of the source.
Mimicking Legitimate Company Websites
Phishing websites often go to great lengths to mimic the look and feel of legitimate company websites. They may use similar logos, color schemes, and website layouts to trick users into believing they’re on the real website. This technique is known as “spoofing.”
Visual Guide: Legitimate vs. Phishing Website
Imagine two websites side-by-side. The legitimate websitewould have a clean, professional design with a secure HTTPS connection (indicated by a padlock icon in the address bar). The URL would match the company’s official website, and the content would be consistent with the company’s brand and messaging.
In contrast, the phishing websitemight have a slightly off design, a missing padlock icon, a suspicious URL, and content that seems generic or out of place.
Unusual Payment Methods

While some payment methods are commonplace in the business world, others are rarely used by legitimate employers, especially when it comes to hiring new employees. Job seekers should be wary of any job offers that request unusual payment methods, as this is a common tactic used by scammers to steal personal information and money.
Payment Methods Rarely Used by Legitimate Employers
Legitimate employers generally use established and secure payment methods for payroll and other business transactions. They are less likely to use unconventional methods that could raise security concerns. Here are some payment methods that are often associated with phishing schemes:
- Wire Transfers:While wire transfers are sometimes used for large business transactions, they are not a typical method for paying employees. They are often used by scammers because they are difficult to trace and reverse.
- Gift Cards:Gift cards are primarily intended for purchasing goods and services and are not designed for financial transactions. Legitimate employers would not use gift cards to pay employees, as it is a risky and unreliable method.
- Cryptocurrency:While cryptocurrency is gaining popularity, it is still not widely accepted as a standard payment method by most businesses. Scammers may use cryptocurrency to make transactions more difficult to track.
- Cash App or Venmo:These peer-to-peer payment apps are convenient for personal transactions, but they are not typically used for employment payments. They may be used by scammers to disguise their activities.
Examples of Phishing Schemes Involving Unusual Payment Methods, 5 ways to identify job phishing schemes
Scammers may use a variety of tactics to pressure job seekers into using unusual payment methods. Here are some common examples:
- Requesting a “processing fee”: The scammer may ask for a small fee upfront to cover background checks or other administrative costs. This is a common red flag, as legitimate employers typically cover these expenses themselves.
- Claiming a “bonus” or “incentive”: The scammer may offer a large bonus or incentive to convince the job seeker to use a specific payment method, such as a wire transfer or gift card. This is a common tactic to trick job seekers into believing they are getting a good deal.
- Creating a sense of urgency: The scammer may pressure the job seeker to act quickly, claiming that the job offer is time-sensitive. This can make it difficult for the job seeker to carefully consider the payment method being requested.





