1 5m uk jobs now at risk ai report – 1.5M UK jobs now at risk ai report sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The report, a chilling reminder of the transformative power of artificial intelligence (AI), paints a stark picture of the potential job displacement looming on the horizon.
This report isn’t just about numbers; it’s about people, their livelihoods, and the future of work in the UK. It’s about understanding the potential impact of AI on different sectors, analyzing the economic implications, and exploring how we can navigate this complex landscape to ensure a future where technology empowers, not displaces.
The report dives deep into the potential impact of AI across various sectors, highlighting the jobs most vulnerable to automation. It examines the methodologies used to estimate job losses, shedding light on the complex factors driving this trend. But the report doesn’t stop there.
It goes beyond the numbers to explore the broader economic implications, analyzing the potential impact on GDP growth, productivity, and unemployment rates. It also examines the government’s role in mitigating the impact of AI on employment, discussing current policies and initiatives aimed at supporting workers and fostering a future-ready workforce.
The AI Report and its Impact
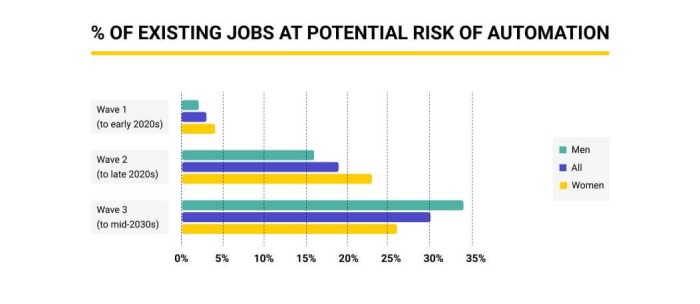
The recent AI report, focusing on the potential job displacement in the UK, paints a stark picture of the future of work. The report highlights the significant impact AI is poised to have on various sectors, leading to job losses and potentially reshaping the employment landscape.
Sectors and Job Roles Most Affected by AI
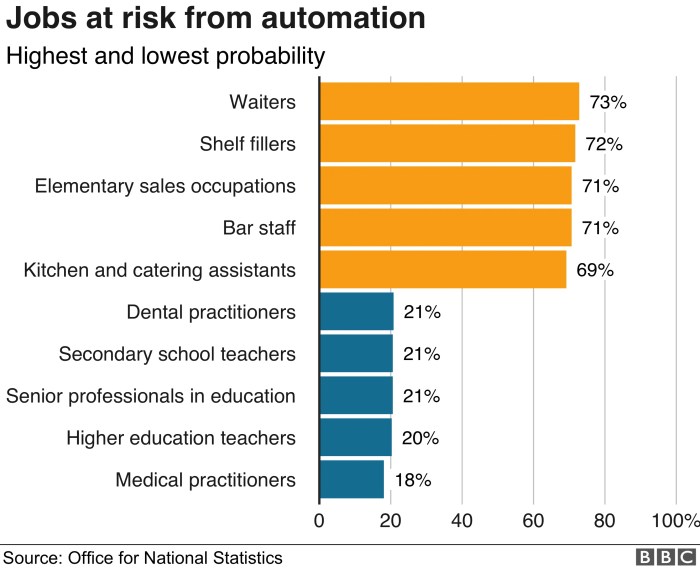
The report identifies several sectors and job roles that are particularly vulnerable to AI automation. These include:
- Manufacturing:AI-powered robots and automated systems are already replacing human workers in manufacturing, particularly in tasks like assembly and quality control.
- Transportation:Self-driving vehicles are expected to disrupt the transportation industry, potentially replacing truck drivers, taxi drivers, and even bus drivers.
- Customer Service:Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by AI are increasingly being used to handle customer inquiries, potentially replacing call center agents and other customer service representatives.
- Finance:AI algorithms are being used to automate tasks like fraud detection, risk assessment, and financial trading, potentially displacing financial analysts and other financial professionals.
- Healthcare:AI is being used to diagnose diseases, develop personalized treatment plans, and even perform surgery, potentially replacing some medical professionals.
Methodology for Estimating Job Risk
The report employs a comprehensive methodology to estimate the number of jobs at risk. This methodology involves:
- Analyzing existing data:The report draws on data from various sources, including government statistics, industry reports, and academic research, to assess the current state of AI adoption and its impact on different sectors.
- Modeling future trends:The report uses sophisticated models to project future trends in AI development and adoption, considering factors such as technological advancements, economic conditions, and regulatory policies.
- Assessing job tasks:The report examines the specific tasks performed in different jobs and assesses the likelihood that these tasks can be automated by AI.
- Estimating job displacement:Based on the analysis of job tasks and the projected adoption of AI, the report estimates the number of jobs that are likely to be displaced in the coming years.
The report emphasizes that while AI is expected to create new jobs in areas like AI development, data science, and AI ethics, the overall impact on employment is likely to be negative, with a significant number of jobs being lost due to automation.
Find out further about the benefits of electric air taxi first untethered test flight that can provide significant benefits.
Impact on the UK Economy
The potential economic impact of AI-driven job displacement in the UK is a complex issue with both positive and negative implications. While AI can boost productivity and economic growth, it also poses risks to employment levels and requires careful policy responses to mitigate these risks.
Potential Economic Implications
The potential economic implications of AI-driven job displacement are multifaceted and require careful consideration. AI can lead to both positive and negative impacts on the UK economy, impacting GDP growth, productivity, and unemployment rates.
Impact on GDP Growth
AI has the potential to significantly boost UK GDP growth by enhancing productivity and creating new industries.
- By automating tasks and processes, AI can increase efficiency and productivity across various sectors, leading to higher output and economic growth. For example, AI-powered robots in manufacturing can increase production speed and accuracy, contributing to economic expansion.
- AI can also drive innovation and the creation of new industries, further contributing to GDP growth. For instance, the development of AI-driven healthcare solutions can create new markets and opportunities for economic expansion.
Impact on Productivity
AI’s ability to automate tasks and improve decision-making processes can significantly enhance productivity across various industries.
- By automating repetitive tasks, AI can free up human workers to focus on more complex and creative endeavors, leading to increased productivity. For example, AI-powered chatbots can handle customer service inquiries, allowing human agents to focus on more complex issues.
- AI can also improve decision-making by analyzing large datasets and identifying patterns that humans might miss. This can lead to better resource allocation, optimized processes, and ultimately, increased productivity. For example, AI-powered systems can analyze financial data to identify investment opportunities and optimize portfolio performance.
Impact on Unemployment Rates
While AI can boost productivity and economic growth, it also poses a risk to employment levels. The automation of tasks can lead to job displacement, potentially increasing unemployment rates.
- Certain jobs, particularly those involving repetitive or routine tasks, are more susceptible to automation. For example, AI-powered systems are already replacing human workers in tasks such as data entry, customer service, and manufacturing.
- The impact on unemployment rates will depend on the pace of AI adoption, the government’s response to job displacement, and the ability of workers to adapt to new skills and job demands.
Comparing Benefits and Risks
The adoption of AI presents both potential benefits and risks to the UK economy. While AI can boost productivity and economic growth, it also poses a risk to employment levels.
- Benefits:AI can drive innovation, create new industries, enhance productivity, and boost GDP growth.
- Risks:AI can lead to job displacement, potentially increasing unemployment rates, and requiring significant investments in education and retraining to ensure workers can adapt to the changing job market.
Government and Industry Response
The UK government and industry are actively responding to the potential impact of AI on employment. While the full extent of AI’s influence is still unfolding, proactive measures are being implemented to mitigate risks and harness opportunities.
Government Policies and Initiatives
The government recognizes the potential for AI to disrupt the labor market and is taking steps to address the challenges and opportunities. Here are some key policies and initiatives:
- The National AI Strategy:Launched in 2021, the strategy aims to make the UK a global AI superpower by investing in research, development, and talent. It includes a focus on supporting the adoption of AI in various sectors, including healthcare, education, and transportation.
- The Future of Work:The government is investing in initiatives to help workers adapt to the changing job market. This includes funding for upskilling and reskilling programs, supporting digital literacy, and promoting flexible work arrangements.
- The Centre for Data Ethics and Innovation (CDEI):The CDEI is a government-funded organization that provides guidance on the ethical and responsible use of AI. It works with businesses and policymakers to ensure that AI is developed and deployed in a way that benefits society.
Industry’s Role in Adaptation and Reskilling
Industries are taking various approaches to adapt to AI advancements and prepare their workforce for the future. Here are some key strategies:
- Investment in AI Technologies:Many companies are investing heavily in AI technologies to improve efficiency, automate processes, and gain a competitive edge. This includes implementing AI-powered systems for customer service, data analysis, and product development.
- Reskilling and Upskilling Programs:Forward-thinking companies are investing in training programs to equip their workforce with the skills needed to work alongside AI systems. This includes training in data analysis, programming, and AI-related fields.
- Collaboration with Universities and Research Institutions:Many companies are partnering with universities and research institutions to access cutting-edge AI research and develop innovative solutions. This collaboration helps them stay ahead of the curve and develop the talent they need.
Effectiveness of Current Strategies and Potential Future Actions
While the government and industry are taking important steps, the effectiveness of current strategies is still being evaluated. Future actions will likely focus on:
- Developing a Comprehensive AI Workforce Strategy:This strategy should include a clear roadmap for addressing the skills gap, promoting lifelong learning, and supporting workers transitioning to new roles. It should also consider the potential for AI to create new jobs and opportunities.
- Enhancing AI Education and Training:Expanding access to AI education and training programs at all levels, from primary school to higher education, is crucial. This will help equip future generations with the skills needed to thrive in an AI-driven economy.
- Addressing Ethical and Societal Concerns:Ongoing dialogue and collaboration between policymakers, industry leaders, and researchers are essential to address the ethical and societal implications of AI. This includes issues related to bias, privacy, and the potential for job displacement.
The Future of Work in the UK: 1 5m Uk Jobs Now At Risk Ai Report
The UK’s workforce is on the cusp of a dramatic transformation, driven by the rapid advancements in AI. This technological revolution will reshape the landscape of work, creating new opportunities while simultaneously displacing existing roles. Understanding these changes is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike.
The Evolving Nature of Work
The integration of AI into various sectors is automating tasks previously performed by humans, leading to a shift in the nature of work. AI-powered systems are capable of handling repetitive, data-intensive tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on higher-level skills like creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
New Job Roles and Industries
The rise of AI is not just about replacing jobs; it’s also about creating new ones. As AI technologies mature, new industries and job roles are emerging, driven by the need for skilled professionals to develop, implement, and manage these systems.
Some examples include:
- AI Engineers: These professionals are responsible for designing, building, and deploying AI models and systems.
- AI Data Scientists: They collect, clean, and analyze large datasets to train AI models and extract valuable insights.
- AI Ethics Specialists: As AI systems become increasingly complex, there’s a growing need for professionals who can ensure ethical and responsible development and deployment.
- AI Trainers: These individuals are responsible for teaching AI systems to perform specific tasks, often using large datasets and feedback mechanisms.
Skills and Qualifications for the AI-Powered Future
To thrive in the AI-powered future, workers will need to adapt and acquire new skills. The demand for technical skills like coding, data analysis, and machine learning will continue to rise. However, non-technical skills are equally crucial.
- Problem-solving and critical thinking: AI systems can assist with data analysis and decision-making, but humans are still needed to define problems, interpret results, and make critical judgments.
- Creativity and innovation: AI can automate routine tasks, but it’s human creativity that will drive innovation and create new products and services.
- Adaptability and lifelong learning: The AI landscape is constantly evolving, so workers need to be adaptable and willing to learn new skills throughout their careers.
- Collaboration and communication: As AI systems become more integrated into the workplace, effective collaboration and communication between humans and machines will be essential.
Case Studies
It’s crucial to remember that AI’s impact on jobs is not solely about displacement. Many companies are successfully integrating AI while minimizing job losses and even creating new opportunities. Here are some examples:
Companies Successfully Implementing AI
This section will explore companies that have successfully implemented AI while minimizing job losses. This includes companies across different industries and their approaches to leveraging AI for growth.
| Company Name | Industry | AI Implementation | Job Impact | Success Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | E-commerce | AI-powered recommendations, warehouse automation | Job creation in areas like data science and AI development, but also some displacement in logistics | Investment in retraining and upskilling programs for employees affected by automation, focus on customer experience enhancement |
| John Deere | Agriculture | Autonomous tractors, precision farming tools | Job creation in areas like AI engineering and data analysis, but also some displacement in traditional farm labor | Partnership with universities and research institutions for talent development, focus on efficiency and productivity improvements |
| Technology | AI-powered search, translation, and advertising | Job creation in areas like AI research and development, but also some displacement in traditional roles like search engine optimization | Emphasis on research and innovation, focus on building a diverse and inclusive workforce |
Individuals Successfully Transitioning Careers
This section will showcase individuals who have successfully transitioned their careers in response to AI advancements. This includes professionals from different backgrounds who have adapted their skills and knowledge to thrive in the evolving job market.This section will showcase examples of individuals who have successfully transitioned their careers in response to AI advancements.
This includes professionals from different backgrounds who have adapted their skills and knowledge to thrive in the evolving job market.
“I was a data entry clerk for a large insurance company. When AI automation started taking over some of my tasks, I realized I needed to upskill. I enrolled in a coding bootcamp and now work as a software developer. The transition was challenging, but I was able to leverage my previous experience and learn new skills to succeed in a different field.”
Sarah, Software Developer
“As a graphic designer, I was worried about AI taking over my job. But I realized that AI can actually be a powerful tool for designers. I started learning how to use AI-powered design tools and now I’m able to create more complex and innovative designs. It’s actually enhanced my work.”
Michael, Graphic Designer
These individuals demonstrate that career transitions are possible with proactive efforts. They have successfully adapted to the changing job market by embracing new technologies and acquiring new skills.
Strategies for Successful Adaptation and Career Growth
This section will explore the strategies used for successful adaptation and career growth in the face of AI advancements. This includes developing new skills, embracing lifelong learning, and fostering a mindset of adaptability.
- Develop new skills:Identify the skills that are in high demand in the AI-driven economy, such as data analysis, programming, and AI ethics. Consider online courses, bootcamps, or university programs to acquire these skills.
- Embrace lifelong learning:The job market is constantly evolving, so it’s crucial to stay ahead of the curve by continuously learning new skills and technologies. This can be achieved through online courses, workshops, conferences, and industry publications.
- Foster a mindset of adaptability:Be open to new opportunities and challenges. Embrace the idea that your career path may not be linear and be willing to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Network and build relationships:Connect with professionals in your field and other industries to learn about emerging trends and potential career opportunities. Attend industry events, join professional organizations, and use online platforms to expand your network.
Public Perception and Concerns
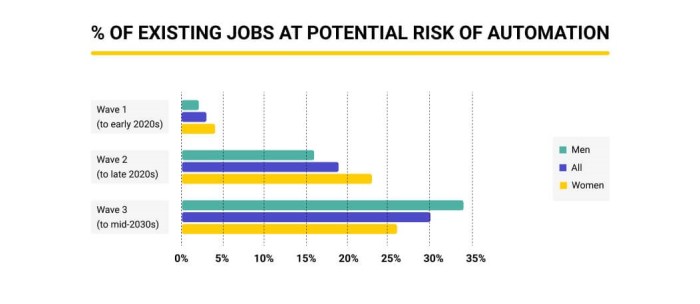
The public’s perception of AI is a complex tapestry woven from threads of excitement, apprehension, and uncertainty. While many recognize the potential benefits of AI in various sectors, there is also a growing awareness of its potential impact on employment.
This section explores the public’s views on AI and its implications for the workforce, highlighting key concerns and anxieties surrounding job displacement.
Public Perception of AI and Employment, 1 5m uk jobs now at risk ai report
The public’s perception of AI’s impact on employment is nuanced. While there is a general understanding that AI could automate certain tasks, there is also a range of opinions on the extent and speed of this automation. Some individuals believe that AI will create new jobs and opportunities, while others fear widespread job displacement and economic instability.
- A 2023 survey by the Pew Research Center found that 72% of Americans believe that AI will eventually lead to widespread job displacement, with 37% believing this will happen within the next 50 years.
- However, the same survey also found that 62% of Americans believe that AI will create new jobs and opportunities, with 29% believing this will happen within the next 50 years.
This suggests that the public is aware of the potential for both positive and negative impacts of AI on employment, with a significant portion expressing concern about job displacement.
Key Concerns and Anxieties Surrounding AI Job Displacement
Public concerns surrounding AI job displacement can be categorized into several key areas:
- Job Security:The fear of losing one’s job to automation is a primary concern for many. This anxiety is particularly acute among those working in sectors identified as being highly susceptible to AI automation, such as manufacturing, transportation, and customer service.
- Income Inequality:There is a concern that AI-driven automation could exacerbate existing income inequality by displacing low-skilled jobs and creating a demand for highly skilled workers, leaving many individuals unable to adapt and compete in the changing job market.
- Skill Gaps:The rapid pace of technological advancement presents a challenge for individuals to acquire the skills necessary to thrive in an AI-driven economy. This concern highlights the need for effective education and training programs to equip workers with the skills required for the jobs of the future.
- Ethical Concerns:The public is increasingly concerned about the ethical implications of AI, including the potential for bias, discrimination, and lack of transparency in decision-making processes. These concerns raise questions about the need for robust regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines for the development and deployment of AI technologies.
Addressing Public Concerns and Building Trust in AI
Addressing public concerns and building trust in AI requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Open and Transparent Communication:Open and transparent communication about the potential impacts of AI is crucial. This includes providing clear information about the capabilities and limitations of AI technologies, the types of jobs that are most likely to be affected, and the strategies being implemented to mitigate job displacement.
- Investment in Education and Training:Investing in education and training programs that equip workers with the skills necessary to thrive in an AI-driven economy is essential. These programs should focus on developing skills in areas such as data analysis, programming, and critical thinking.
- Support for Workers:Providing support for workers who are displaced by AI automation is crucial. This includes providing access to retraining programs, unemployment benefits, and job placement services.
- Ethical Guidelines and Regulations:Developing and implementing ethical guidelines and regulations for the development and deployment of AI technologies is essential. This includes addressing concerns about bias, discrimination, and transparency in AI decision-making processes.
- Public Engagement:Engaging the public in discussions about the future of work and the role of AI is vital. This includes involving diverse stakeholders, including workers, policymakers, and industry leaders, in shaping the development and deployment of AI technologies.